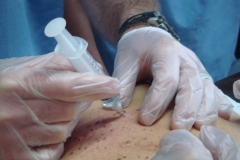
Novel Sonoguided Digital Palpation and Hydrodissection for Sural Nerve Dysfunction Mimicking Achilles Tendinopathy in a Psoriasis Patient
Yonghyun Yoon, King Hei Stanley Lam, Howon Lee, Chanwool Park, Seungbeom Kim, Minjae Lee, Jaeyoung Lee, Jihyo Hwang, Hyemi Yu, Jonghyeok Lee, Daniel Chiung-Jui Su, Teinny Suryadi, Anwar Suhaimi and Kenneth Dean Reeves
Diagnostics 2025, 15(21), 2706
Abstract
Background and Clinical Significance: Psoriasis, a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease, can affect musculoskeletal structures, including the Achilles tendon. Achilles pain in psoriasis patients may arise from tendinitis or neuropathic pain due to peripheral nerve dysfunction, such as sural nerve (SN) involvement, a condition frequently misdiagnosed due to limitations in conventional diagnostics. Fascial tissues are critical in nerve compression syndromes. This case explores the application of a novel quantitative Sonoguide Digital Palpation (SDP) protocol and ultrasound (US)-guided hydrodissection (HD) for SN dysfunction mimicking Achilles tendinopathy in a psoriasis patient.
Case Presentation: A 41-year-old male with psoriasis presented with acute onset of right heel stiffness and paresthesia. Physical examination, radiographs, and ultrasound were performed. SDP, employing a validated four-criterion diagnostic framework (including fascial mobility quantification and concordant pain provocation), identified crural fascia restriction affecting SN and reproduced patient’s concordant Achilles pain. High-resolution ultrasonography provided key morphological evidence, revealing a 2.6-fold enlargement of the sural nerve’s cross-sectional area (CSA) on the affected side (13 mm2) compared to the asymptomatic side (5 mm2). Notably, a positive Tinel’s sign was elicited over the psoriatic plaque. US-guided HD was performed using 50 cc of 5% dextrose in water (D5W) without local anesthetic below the psoriatic lesion. Post-HD, the patient reported immediate and significant pain relief (Numeric Pain Rating Scale (NPRS) score reduction from 8 to 2), confirming the prompt correction of a clinically important fascial restriction, associated with improved SN mobility, objectively verified by a post-procedure SDP assessment. At 24-month follow-up, sustained symptom relief and complete functional recovery were reported.
Conclusions: This case highlights SDP’s ability to objectively visualize and confirm fascial restriction as a cause of nerve dysfunction by quantitatively reproducing concordant pain. The objective finding of nerve swelling provides sonographic substantiation for the functional diagnosis of nerve dysfunction. This integrated diagnostic approach, combining dynamic functional assessment with morphological confirmation, offers a novel paradigm for evaluating peripheral nerve disorders. US-guided HD of the SN with D5W without local anesthetic shows promise as both a diagnostic confirmatory tool and therapeutic intervention for neuropathic Achilles pain in psoriasis patients with SN involvement, aligning with its efficacy in other peripheral neuropathies. The significant nerve swelling (13 mm2) provides robust morphological corroboration of the functional impairment diagnosed by SDP, offering a more comprehensive diagnostic paradigm.
Keywords: psoriasis; sural nerve dysfunction; Sonoguide Digital Palpation; ultrasound-guided hydrodissection; Achilles tendinopathy; psoriasis-associated neuropathy; neuropathic foot pain; 5% dextrose in water; crural fascia; fascial restriction
Annual Scientific Meeting 2025
Date: 13 - 14 September 2025 (Saturday - Sunday)
Diploma of Musculoskeletal Medicine 2025 - 2027
Registration Deadline: 31 August 2025
Enquiry: hkimmltd@gmail.com