Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
 Dynamic ultrasound imaging
Dynamic ultrasound imagingDynamic ultrasound imaging
The ultrasound examination is dynamic because it is performed in real time, showing motion live with patient’s interaction. The musculoskeletal physician can put the patient in motion to reproduce the pain or symptoms and focus on that region under real-time ultrasound to find out its causative structure or mechanism. The result is a more directed examination, specific for each individual.
Dynamic ultrasound imaging is a rapidly developing, powerful diagnostic tool in musculoskeletal medicine. Compared to other cross-sectional imaging modalities, ultrasound has several inherent advantages: ready accessibility, portability, quick scan time, and better patient tolerability. Newer innovative features such as tissue harmonics and 3-D imaging may be helpful in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal disorders in future.
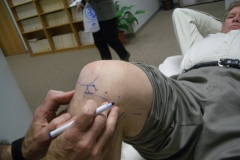
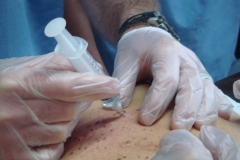
Ultrasound guided injections
In the days before musculoskeletal ultrasound is available, sites for joint injections can only be located by palpations which are often inaccurate. Eustace, (1997)1 and Yamakado (2002)2 have demonstrated poor accuracy of steroid placement from palpation guided injection techniques.
High-resolution ultrasound has proven accurate and reliable in diagnosing a wide range of musculoskeletal disorders compared with clinical examination, MRI and arthrogram. (Dinnes, Loveman, McIntyre and Waught 2003)3.
With the help of these high-resolution ultrasound machines, injections can be placed under direct ultrasound monitoring exactly to the spot where the injection is plan to be placed. It's accuracy, safety, and simplicity has been widely described. (Koski 20004, Balint 20025, Naredo 20046). Advantages include short procedural time, no limitation on imaging plane, relatively low cost, lack of ionizing radiation and more readily available.
References:
肌骼超聲波掃描
 動態肌骼超聲波掃描
動態肌骼超聲波掃描動態肌骼超聲波掃描
超聲波掃描之所以稱為動態掃描,是因為它是實時進行的掃描,也就是即時顯示出病人活動時的動作影像與過程。肌骼科醫生可以讓病人活動身體部位,令痛症或症狀重現,然後集中於該部位進行實時的超聲波掃描,以找出其致病的結構及病因。這是一種更直接、更個人化的檢查方法。
動態肌骼超聲波掃描是一個迅速發展的強大肌骼科診斷工具。相比其他橫切面圖像掃描,動態肌骼超聲波本身有幾項優點:隨時可用、可移動性、掃描時間快速及病人容易接受。新一代超聲波掃描的創新功能,例如組織諧波和三維圖像掃描,在肌骼疾病的診斷方面,將來可能會發揮更大的作用。
超聲波掃描引導下的注射療法
在肌骼超聲波發明之前,醫生只能靠觸感找出體位作注射治療,但很多時注射的位置是不準確的。Eustace (1997)1 和Yamakado (2003)2 的研究就顯示了觸感引導下注射類固醇的位置的不準確度。
與臨床檢查、磁力共振掃描、關節內窺鏡檢查相比較,高清晰度超聲波掃描已被證明可以更準確及可靠地診斷各式各樣的肌骼科疾病 (Dinnes, Loveman, Mclntyre and Waught 2003)3。
有了這些高清晰度超聲波儀器的幫助,注射治療可以在超聲波掃描的導航下做到更準確,甚至能夠直達患處。它的準確性、安全性和簡單性已被廣泛肯定 (Koski 20004, Blaint 20025, Naredo 20046)。
超聲波掃描引導下的注射療法的優勢包括:程序省時、沒有平面圖像的限制、成本相對較低、沒有電離輻射及隨時可用。
參考文獻: